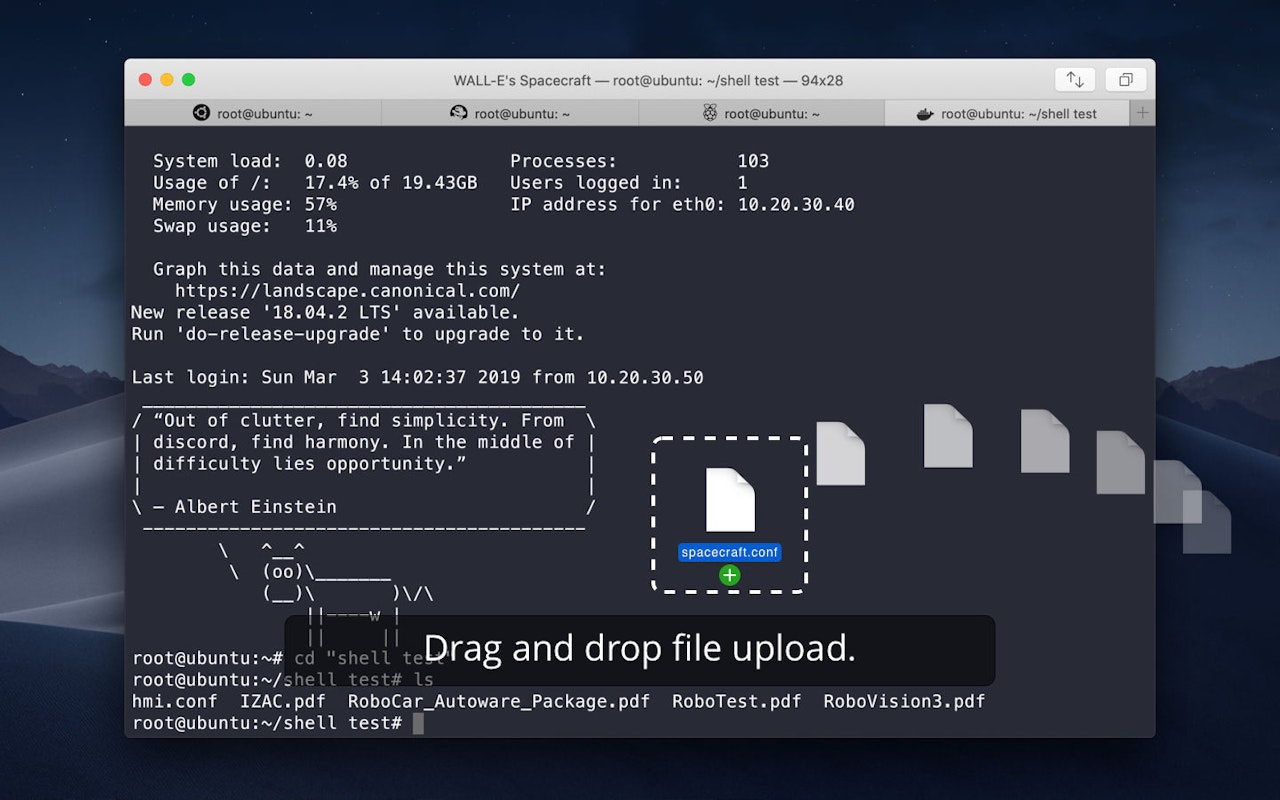
Get a Static IP Address on your Mac: The first step to setting up these web services on your. It's the default terminal emulator that comes embedded in the Mac OS.
WinOnMacs released Putty for Mac 9.1.1 for MacOS today. Putty 9.1.1 is a minor release, Please see the full change-log below for all the changes in this release.
Telnet free download - Mocha Telnet, Putty for Mac, NiftyTelnet SSH, and many more programs. Telnet client ZOC is a professional telnet client and ssh terminal emulator for Windows and Mac OS. Find out more about this telnet client. Mail clients for mac os. Telnet is a standard protocol for connecting computers. ZOC is a powerful telnet client and terminal emulator that offers you a wide range of useful features. Read more about telnet and our telnet client.
Putty is one of the Best Terminal Emulators available today. It Supports different types of Network Protocols such as SSH, FTP, SCP, Telnet etc. In Windows it is used as SSH Client to connect to Your Linux server or for some other purpose But what will you do if you are on Mac? You might be thinking , Is there any Software like Putty for Mac Available? The answer is Yes! With the help of some other Software's we can Use putty on MacOS although Putty is used widely on Windows Platform. Official Versions of Putty are available on Unix like Platforms, and now it's widely available for Mac systems running OSX 10.12.6 or higher.
SSH is available by default in Mac and Linux or Unix. Although you can use terminal for SSH connections still there are some benefits in using Putty such as Other clients don't keep connections alive whereas Putty does. Also it is cool to use Putty as your SSH client if you are doing some Amazon AWS, VMware ESXi or CISCO Stuffs, transferring files, managing files on a server or whatever.
The cost of Putty 9.1.1 is only $15.00. A Subscription plan is also available that comes with one year of free upgrades . Putty also comes with a standard 14-day money back guarantee.
Supported Protocols:
- Telnet
- FTP
- SFTP
- SSH
- SCP
About WinOnMacs:
There is a multitude of software developed only for the Windows operating system and even when software vendors port their applications to another platform, generally it lacks features that the Windows version contains. The only solution these developers face is to have access to both systems for testing which leads to increased infrastructure demands, and wasted project resources. Our goal is to have native ports of essential Windows tools and applications made available for MacOS users.
Version 9.1.1 New Features:
- macOS 10.14.5 Mojave support
- Minor bug fixes
We now use FastSpring as our preferred storefront, you can pay with Credit / Debit Cards, PayPal, Amazon payments, Wire Transfer etc. etc. This store is very secure, simple and fast.
Purchase Putty 9.1.1 now and have Telnet SSH FTP SCP on your Mac made easy!
Updates
About
Open source MAC Telnet client and server for connecting to Mikrotik RouterOS routers and Linux machines via MAC address.
Based on MAC-Telnet the original work of haakonnessjoen ( Håkon Nessjøen );forked the upstream version to add forwarding mode for tunneling a TCP connection through MAC-Telnet protocol, and implemented MAC-SSH client and server functionality for tunneling SSH protocol instead of implementing shell interface directly.
Unless you will be using any of the additional functionalities, I recommend using the Original Version fromhaakonnessjoen ( Håkon Nessjøen ) instead.
Ssh Telnet Macos
For information on other projects you can check my GitHub Personal Pageand GitHub Profile.
Differences
The original version implements the following:
- A Linux console tool for connecting to MikroTik RouterOS devices via theirEthernet address.
- Linux daemon that implements the MAC-Telnet server to permit connectingto Linux machines via their ethernet address.
The forked version implements additional functionality for forwarding a TCP connection through the MAC Telnet protocol. The main use case is connecting to Linux machines via their Ethernet address using the SSH protocol for security. Take note that the clients and servers running in theforwarding mode are not compatible with existing MAC-Telnet clients and servers implementing the standard mode of operation.
The forked version of the server supports two modes of operation:* Standard MAC-Telnet Server Mode* TCP Connection Forwarding Mode: Tunnels a TCP connection to a local port on the client to a specific local port on the server side through MAC-Telnet protocol. This mode of operation is used for forwarding SSH connections through the MAC-Telnet protocol.
The client supports three modes of operation:* Standard MAC-Telnet Client Mode* TCP Connection Forwarding Mode: Tunnels a specific local port on the client to the serverthrough MAC-Telnet protocol.* SSH Forwarding Mode: Apart from setting up the tunnel, the client takes care of launching the SSH client.
The SSH Forwarding Mode has the following advantages in comparison to standardMAC-Telnet:
- The_mactelnet.users_ configuration file is not needed. Instead of maintaining another set of user passwords for MAC-Telnet, the authentication mechanisms implemented ssh are used.
- Public Key Authentication works seamlessly permiting passwordless logins.
- The communication between client and server is encrypyted by SSH.
- The daemon does not require root privileges and can be run by a non-privileged user for additional security. In case the -n option is used, the serveror client must be launched as root user, but the-U option can be used to drop privileges once the initial setup phase ends.
- The server relies on the security model of SSH, instead of creating a shellenvironment itself.
Use Cases
Embedded Systems
It can be used for initial provisioning and for maintenance purposes in situations where a valid IP configuration is not available.
Might be a useful addition to the rescue mode especially of embedded systems without screens; connecting using MAC-Telnet / MAC-SSH is much more convenient then fetching and connecting a serial cable.
The Datacenter
It can be used for initial provisioning of physical and virtual servers and might serve as a rescue system, when the IP configuration of a server gets messed up for any reason.
Download
Binary Packages
The original version of the MAC-Telnet has been packaged for Debian GNU/Linuxby the original author haakonnessjoen ( Håkon Nessjøen ).You can download the deb packages for the original version from the Downloads Page of the Upstream Project.
Source Packages
The original version of the MAC-Telnet by haakonnessjoen ( Håkon Nessjøen ) canbe download from the project page of the Upstream Project.
You can download the latest development version of this code that is hosted at GitHub eitherin ZIPor TAR format.
You can also get the latest development version of the code by cloning the Git repository for the project by running:
Installation
The binary packages of the original version of the code can be installed using the packaging tools of the distribution.
Once the source code is cloned or downloaded it can be installed as follows:
Configuration
Sample upstart configuration files can be found in the config directory ofthe distribution:
- Use mactelnetd.init for starting / stopping MAC-Telnet in standard mode.
- Use macsshd.init for starting / stopping MAC-Telnet in MAC-SSH mode.
Usage
mactelnet
Usage
Examples
Establish standard MAC-Telnet session with remote box:
Forward local port 4001:
Establish SSH connection with remote box:
Establish SSH connection with remote box, forwarding additional ports using SSH Port Forwarding:
mactelnetd
Usage
Examples
Launch MAC-Telnet Daemon for receiving Standard MAC-Telnet protocol connections:
Launch MAC-Telnet Daemon for forwarding connections to local SSH Daemon listening on port 22:
Launch MAC-Telnet Daemon for forwarding connections to local SSH Daemon listeningon non-standard port 2222:
macping
Usage
Examples
mndp
Usage
Examples
Troubleshooting
Disable firewalls both on the client and server side for testing. Firewalls can block the forwarding of packets with broadcast addresses even when they arenot blocking any ports.
The server can be run in the foreground (commanline option: -f) for testing.
Credits
Ssh Telnet Macos
For information on other projects you can check my GitHub Personal Pageand GitHub Profile.
Differences
The original version implements the following:
- A Linux console tool for connecting to MikroTik RouterOS devices via theirEthernet address.
- Linux daemon that implements the MAC-Telnet server to permit connectingto Linux machines via their ethernet address.
The forked version implements additional functionality for forwarding a TCP connection through the MAC Telnet protocol. The main use case is connecting to Linux machines via their Ethernet address using the SSH protocol for security. Take note that the clients and servers running in theforwarding mode are not compatible with existing MAC-Telnet clients and servers implementing the standard mode of operation.
The forked version of the server supports two modes of operation:* Standard MAC-Telnet Server Mode* TCP Connection Forwarding Mode: Tunnels a TCP connection to a local port on the client to a specific local port on the server side through MAC-Telnet protocol. This mode of operation is used for forwarding SSH connections through the MAC-Telnet protocol.
The client supports three modes of operation:* Standard MAC-Telnet Client Mode* TCP Connection Forwarding Mode: Tunnels a specific local port on the client to the serverthrough MAC-Telnet protocol.* SSH Forwarding Mode: Apart from setting up the tunnel, the client takes care of launching the SSH client.
The SSH Forwarding Mode has the following advantages in comparison to standardMAC-Telnet:
- The_mactelnet.users_ configuration file is not needed. Instead of maintaining another set of user passwords for MAC-Telnet, the authentication mechanisms implemented ssh are used.
- Public Key Authentication works seamlessly permiting passwordless logins.
- The communication between client and server is encrypyted by SSH.
- The daemon does not require root privileges and can be run by a non-privileged user for additional security. In case the -n option is used, the serveror client must be launched as root user, but the-U option can be used to drop privileges once the initial setup phase ends.
- The server relies on the security model of SSH, instead of creating a shellenvironment itself.
Use Cases
Embedded Systems
It can be used for initial provisioning and for maintenance purposes in situations where a valid IP configuration is not available.
Might be a useful addition to the rescue mode especially of embedded systems without screens; connecting using MAC-Telnet / MAC-SSH is much more convenient then fetching and connecting a serial cable.
The Datacenter
It can be used for initial provisioning of physical and virtual servers and might serve as a rescue system, when the IP configuration of a server gets messed up for any reason.
Download
Binary Packages
The original version of the MAC-Telnet has been packaged for Debian GNU/Linuxby the original author haakonnessjoen ( Håkon Nessjøen ).You can download the deb packages for the original version from the Downloads Page of the Upstream Project.
Source Packages
The original version of the MAC-Telnet by haakonnessjoen ( Håkon Nessjøen ) canbe download from the project page of the Upstream Project.
You can download the latest development version of this code that is hosted at GitHub eitherin ZIPor TAR format.
You can also get the latest development version of the code by cloning the Git repository for the project by running:
Installation
The binary packages of the original version of the code can be installed using the packaging tools of the distribution.
Once the source code is cloned or downloaded it can be installed as follows:
Configuration
Sample upstart configuration files can be found in the config directory ofthe distribution:
- Use mactelnetd.init for starting / stopping MAC-Telnet in standard mode.
- Use macsshd.init for starting / stopping MAC-Telnet in MAC-SSH mode.
Usage
mactelnet
Usage
Examples
Establish standard MAC-Telnet session with remote box:
Forward local port 4001:
Establish SSH connection with remote box:
Establish SSH connection with remote box, forwarding additional ports using SSH Port Forwarding:
mactelnetd
Usage
Examples
Launch MAC-Telnet Daemon for receiving Standard MAC-Telnet protocol connections:
Launch MAC-Telnet Daemon for forwarding connections to local SSH Daemon listening on port 22:
Launch MAC-Telnet Daemon for forwarding connections to local SSH Daemon listeningon non-standard port 2222:
macping
Usage
Examples
mndp
Usage
Examples
Troubleshooting
Disable firewalls both on the client and server side for testing. Firewalls can block the forwarding of packets with broadcast addresses even when they arenot blocking any ports.
The server can be run in the foreground (commanline option: -f) for testing.
Credits
MAC-Telnet has originally been developed by haakonnessjoen ( Håkon Nessjøen ).
The code published on this page is a fork with some experimental features forestablishing SSH connections via MAC Address. The additional features have been implemented
by Ali Onur Uyar ([aouyar @ GitHub] (https://github.com/aouyar)).
Ssh And Telnet Client For Mac
License
MAC-Telnet is copyrighted free software made available under the terms of the GPL License Version 3 or later.
Ssh Telnet For Mac High Sierra
See the file LICENSE that acompanies the code for full licensing information.
